Runner system connects the sprue via the gate with the cavity. It has to distribute molten plastics in the same condition, pressure and time for all cavities.
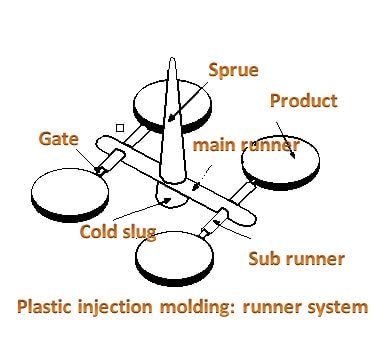
1. The functions of runner.
+ Guides molten plastics into the cavity of a mold with the shortest way and with a minimum of heat and pressure loss.
+ Molten plastics must enter a cavity (or cavities) at all gates at the same time under the same pressure and temperature.
+ For material savings, cross-section should be kept small. Although a large cross-section may be more favorable for optimum cavity filling and maintaining adequate holding pressure. However, larger cross-section may increase cooling time.
+ Surface-over-volume ratio should be kept as small as feasible.
2. What do you care when design runner of injection mold.
In molding design, we must care volume of part, heavy of part, number of cavities, wall thickness, length of flow part, plastics material,… You need to determine the shapes, dimensions, and positions of the runner.
| Items affecting runners. | |
| – Part volume. – Wall thickness. – Plastic material. – Length of follow path. – Resistance to flow. – Surface/volume ratio. |
– Heat losses – Losses from friction. – Cooling time. – Amount of scrap. – Cost of manufacturing. – Mold type (Cold or hoe runner mold). |
3. Cross section area of runner.
Cross section of runner depends on the heat loss, pressure loss, machining requirement. There are three types of runner cross section: circular, parabolic and trapezoid section area.
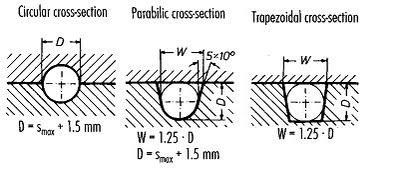
4. Size of Runner
+ Size of runner is following thickness, type of plastics, length, cycle time, maximum injection pressure, packing, and degradation. Diameter of runner usually is 3mm~15mm.
+ We can calculate diameter of runner following the formula.
Ds=(W½*L¼)/3.7 (1)
Ds= sub runner diameter (mm).
W= part weight (g).
L= runner length (mm).
+ If mold has many sub runner, diameter of main runner can calculate following the formula.
Dm=Ds*N⅓
Dm: Diameter of main runner (mm).
Ds: Diameter of sub runner.
N: Quantity of sub runner.
This is runner diameters for unfilled generic materials.
| Material | Diameter (mm) | Material | Diameter (mm) | |
| ABS, San | 5~10 | Polycarbonate. | 5~10 | |
| Acetal. | 3~10 | Thermoplastic polyester. (unreinforced) |
3~8 | |
| Acetate. | 5~11 | Thermoplastic polyester. (reinforced) |
5~10 | |
| Acrylic. | 8~10 | Polyethylene. | 2~10 | |
| Butyrate. | 5~10 | Polyamide. | 5~10 | |
| Fluorocarbon. | 5~10 | Polyphenylene oxide. | 6~10 | |
| Impact acrylic. | 8~13 | Polypropylene. | 5~10 | |
| Ionomers. | 2~10 | Polystyrene. | 3~10 | |
| Nylon. | 2~10 | Polysulfone. | 6~10 | |
| Phenylene. | 6~10 | Polyvinyl. | 3~10 | |
| Phenylene sulfide. | 6~13 | PVC Rigid. | 6~16 | |
| Polyallomer. | 5~10 | Polyurethane. | 6~8 |
5. Layout of runner system.
There are three type of runner layout.
+ “H” bridge (branching) runner system.
+ Standard (herringbone) runner system (conventional runner).
+ Radial (star) runner system.

Thanks for the sharing this post with us i really like your blog. Plastic injection molding is our expertise and what we focus on. Over the years, we have built our business on this core principle. Our 36,000 square foot facility houses over 23 injection molding machines and we are constantly adding and updating our equipment. These machines range from 22 to over 500 tons and many are electric and microprocessor controlled.
Thanks a lot for providing valuable information.