When you design a product for plastic molding, you must care many point : quality, cycle of product, material, injection machine, liquidity, mold designing condition,… In this lesson, i will explain about: Thickness of sample, sharp corner, rib of sample,…
1. Plastic molding: thickness of sample.
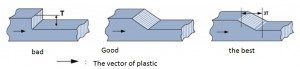
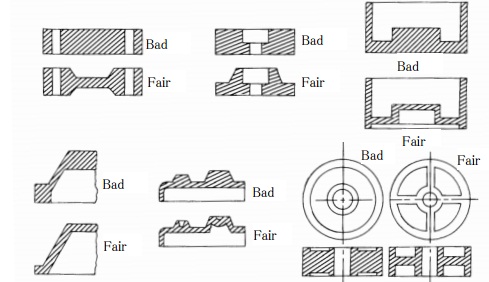
Thickness of sample about 0.5~4 mm and we always want thinner thickness if can.If thickness of sample is too thick, samples will have defect as:
+ it will be the cause of defect: sink mark, short shot,…
+ It will take time to cold up and the mold cycle will be longer.
+ To spend much on production is up.
Example for design thickness:
2. Plastic molding: sharp corner.
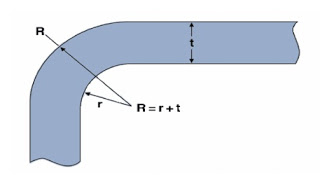
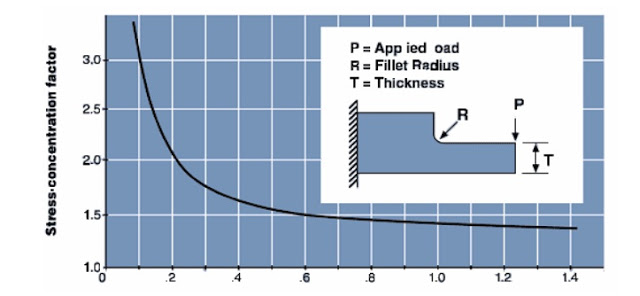
Sharp corner will block the resin flow when molding , which will become a cause of flow marks.The stress will concentrate on the sharp corner part.
Result when we make radius for sample:
+ The stress will down
+ The resin flow will better.
+ Warping of product: defect rate of product will down.
+ The molten plastics will insert to mold better.
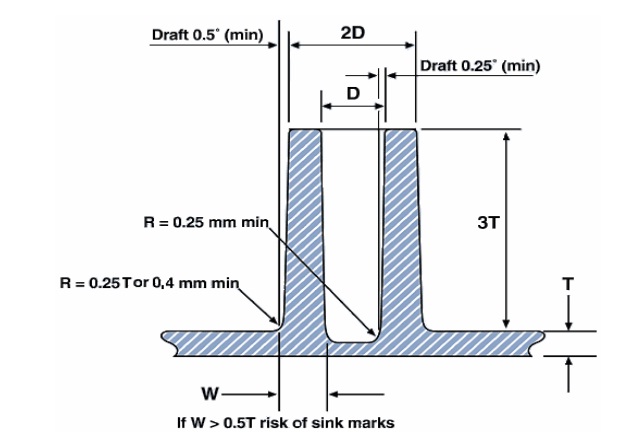
3. Plastic molding: Rib of sample.
Ribs is the part of product which to increase the durability for product.Many times the stiffness of a part must increase because of the load applied to the part design. One of the easiest ways to cure this problem is change the part geometry by adding ribs. The use of ribs is a practical way and economical means of increasing the structural strength of a part.
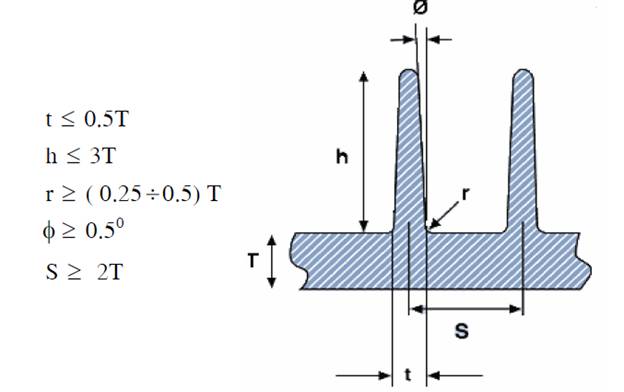
When you design rib of product, you must care:
+ Rib thickness should be less than wall thickness.
+ Don’t make the rib too thick. If part need increase stiffness, please increase number of rib.
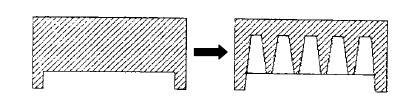
+ For a given stiffness, it is better to increase the number of ribs, not the height.
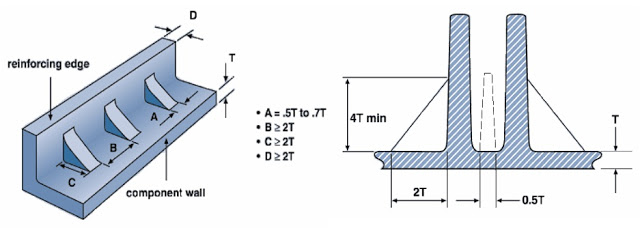
+ For thick ribs ” core out ” the rib from the back. This creates a hollow space underneath the part and maintains a uniform wall thickness.
+ Layer of ribs:
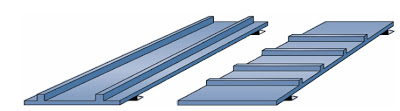
The ribs for a given stiffness.

Leave a Reply